Explodable 3D Dog Skull for Veterinary Education
3D models of a Sheep and Goat Skull and Inner ear
3D models of Miocene vertebrates from Tavers
3D GM dataset of bird skeletal variation
Skeletal embryonic development in the catshark
Bony connexions of the petrosal bone of extant hippos
bony labyrinth (11) , inner ear (10) , Eocene (8) , South America (8) , Paleobiogeography (7) , skull (7) , phylogeny (6)
Lionel Hautier (23) , Maëva Judith Orliac (21) , Laurent Marivaux (16) , Rodolphe Tabuce (14) , Bastien Mennecart (13) , Renaud Lebrun (12) , Pierre-Olivier Antoine (12)

|
3D models related to the publication: “Trophic differentiation between the endemic Cypriot mouse and the house mouse: a study coupling stable isotopes and morphometrics”
|

|
M3#15843D model of the right mandible Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1584 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus cypriacus Cypriacus_BET2 View specimen

|
M3#15853D model of the right mandible Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1585 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus cypriacus Cypriacus_FON1 View specimen

|
M3#15863D model of the right mandible Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1586 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus cypriacus Cypriacus_FON2 View specimen

|
M3#15873D model of the right mandible Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1587 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus cypriacus Cypriacus_KOU1 View specimen

|
M3#15883D model of the right mandible Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1588 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus Cyprus_dom_KOF1 View specimen

|
M3#15893D model of the right mandible Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1589 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus Cyprus_dom_LEF1 View specimen

|
M3#15903D model of the right mandible Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1590 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus Cyprus_dom_MEN1 View specimen

|
M3#15913D model of the right mandible Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1591 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus Cyprus_dom_TSE2 View specimen

|
M3#15923D model of the mirrored left mandible Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1592 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus Cyprus_dom_XYL5 View specimen

|
M3#15933D model of the right mandible Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1593 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
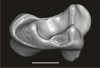
In this work, we digitally restore the snout of the raoellide Khirtharia inflata from the Kalakot area (Rajouri District, Jammu & Kashmir, India). Raoellids are small, semiaquatic ungulates closely related to cetaceans. The specimen is fairly complete and preserves left and right maxillaries, left premaxillary, and part of the anterior and jugal dentition. The digital restoration of this quite complete but deformed specimen of Khirtharia inflata is a welcome addition to the data available for raoellids and will be used to further the understanding of the origins of cetaceans.
Khirtharia inflata GU/RJ/157 View specimen

|
M3#1454deformed partial skull Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1454 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#1455reconstruction of half snout Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1455 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#1456reconstruction of complete snout Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1456 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
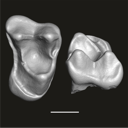
This contribution contains the three-dimensional digital model of one isolated fossil tooth of an anthropoid primate (Ashaninkacebus simpsoni), discovered in sedimentary deposits located on the upper Rio Juruá in State of Acre, Brazil (Western Amazonia). This fossil was described, figured and discussed in the following publication: Marivaux et al. (2023), An eosimiid primate of South Asian affinities in the Paleogene of Western Amazonia and the origin of New World monkeys. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2301338120
Ashaninkacebus simpsoni UFAC-CS 066 View specimen
|
M3#1114Right first upper molar (rM1), pristine. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1114 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

The present 3D Dataset contains the 3D models analyzed in Pochat-Cottilloux Y., Martin J.E., Jouve S., Perrichon G., Adrien J., Salaviale C., de Muizon C., Cespedes R. & Amiot R. (2021). The neuroanatomy of Zulmasuchus querejazus (Crocodylomorpha, Sebecidae) and its implications for the paleoecology of sebecosuchians. The Anatomical Record, https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.24826
Zulmasuchus querejazus MHNC 6672 View specimen

|
M3#798Left endosseous labyrinth of Z. querejazus (MHNC 6672). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.798 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#799Reconstruction of the endocranial cavities of Z. querejazus (MHNC 6672). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.799 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#800Three-dimensional reconstruction of the pneumatic cavities within the braincase of Z. querejazus (MHNC 6672) Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.800 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

The present 3D Dataset contains the 3D models of the holotype and the paratypes of the new species Siphonodella leiosa described and analyzed in the following publication: L. Souquet, C. Corradini, C. Girard: Siphonodella leiosa (Conodonta), a new unornamented species from the Tournaisian (lower Carboniferous) of Puech de la Suque (Montagne Noire, France). Geobios, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geobios.2020.06.004.
Siphonodella leiosa UM PSQ 1 View specimen

|
M3#525Siphonodella leiosa, paratype, dextral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.525 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Siphonodella leiosa UM PSQ 2 View specimen

|
M3#526Siphonodella leiosa, holotype, dextral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.526 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Siphonodella leiosa UM PSQ 3 View specimen

|
M3#527Siphonodella leiosa, paratype, dextral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.527 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Siphonodella leiosa UM PSQ 4 View specimen

|
M3#528Siphonodella leiosa, paratype, dextral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.528 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Siphonodella leiosa UM PSQ 5 View specimen

|
M3#529Siphonodella leiosa, paratype, sinistral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.529 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Siphonodella leiosa UM PSQ 6 View specimen

|
M3#530Siphonodella leiosa, paratype, dextral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.530 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Siphonodella leiosa UM PSQ 7 View specimen

|
M3#531Siphonodella leiosa, paratype, dextral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.531 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Siphonodella leiosa UM PSQ 8 View specimen

|
M3#532Siphonodella leiosa, paratype, sinistral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.532 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Siphonodella leiosa UM PSQ 9 View specimen

|
M3#533Siphonodella leiosa, paratype, dextral P1 element Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.533 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
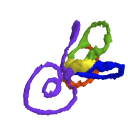
The present 3D Dataset contains the 3D models analyzed in: Toyoda S et al., 2015, Morphogenesis of the inner ear at different stages of normal human development. The Anatomical Record. doi : 10.1002/ar.23268
Homo sapiens KC-CS17IER29248 View specimen

|
M3#36Computationally reconstructed membranous labyrinth of a human embryo (KC-CS17IER29248) at Carnegie Stage 17 (Crown Rump Length= 7mm). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf36 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS18IER17746 View specimen

|
M3#37Computationally reconstructed membranous labyrinth of a human embryo (KC-CS18IER17746) at Carnegie Stage 18 (Crown Rump Length= 12mm). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf37 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS19IER16127 View specimen

|
M3#38Computationally reconstructed membranous labyrinth of a human embryo (KC-CS19IER16127) at Carnegie Stage 19 (Crown Rump Length= 13mm). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf38 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS20IER20268 View specimen
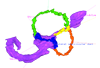
|
M3#39Computationally reconstructed membranous labyrinth of a human embryo (KC-CS20IER20268) at Carnegie Stage 20 (Crown Rump Length= 13.7mm). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf39 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS21IER28066 View specimen

|
M3#40Computationally reconstructed membranous labyrinth of a human embryo (KC-CS21IER28066) at Carnegie Stage 21 (Crown Rump Length= 16.7mm). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf40 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS22IER35233 View specimen
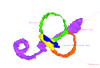
|
M3#41Computationally reconstructed membranous labyrinth of a human embryo (KC-CS22IER35233) at Carnegie Stage 22 (Crown Rump Length= 22mm). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf41 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS23IER15919 View specimen
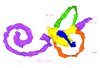
|
M3#42Computationally reconstructed membranous labyrinth of a human embryo (KC-CS23IER15919) at Carnegie Stage 23 (Crown Rump Length= 32.3mm). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf42 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-FIER52730 View specimen
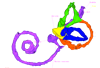
|
M3#43Computationally reconstructed human membranous labyrinth in post embryonic phase (KC-FIER52730). Crown Rump Length: 43.5mm. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf43 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

The present 3D Dataset contains the 3D models analyzed in Merten, L.J.F, Manafzadeh, A.R., Herbst, E.C., Amson, E., Tambusso, P.S., Arnold, P., Nyakatura, J.A., 2023. The functional significance of aberrant cervical counts in sloths: insights from automated exhaustive analysis of cervical range of motion. Proceedings of the Royal Society B. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2023.1592
Ailurus fulgens PMJ_Mam_6639 View specimen

|
M3#1260cervical vertebral series (7 vertebrae) Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1260 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Bradypus variegatus ZMB_Mam_91345 View specimen

|
M3#1261cervical vertebral series (8 vertebrae) + first thoracic vertebra Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1261 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Bradypus variegatus ZMB_Mam_35824 View specimen

|
M3#1262cervical vertebral series (8 vertebrae) + first & second thoracic vertebra Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1262 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Choloepus didactylus ZMB_Mam_38388 View specimen

|
M3#1263cervical vertebral series (7 vertebrae) Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1263 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Choloepus didactylus ZMB_Mam_102634 View specimen

|
M3#1264cervical vertebral series (6 vertebrae) + first thoracic vertebra Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1264 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Tamandua tetradactyla ZMB_Mam_91288 View specimen

|
M3#1266cervical vertebral series (7 vertebrae) + first thoracic vertebra Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1266 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Glossotherium robustum MNHN_n/n View specimen

|
M3#1267cervical vertebral series (7 vertebrae) + first thoracic vertebra Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1267 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

The present 3D Dataset contains the 3D models illustrated and described in the chapter “Paleoneurology of Artiodactyla, an overview of the evolution of the artiodactyl brain” (Orliac et al. 2022) published in "Paleoneurology of amniotes: new directions in the study of fossil endocasts", edited by Dozo, Paulina-Carabajal, Macrini and Walsh.
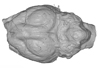
Homacodon vagans AMNH 12695 View specimen
|
M3#1063Endocranial cast Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1063 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
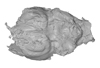
Helohyus sp. AMNH 13079 View specimen
|
M3#1064Endocranial cast Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1064 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Leptauchenia sp. AMNH 45508 View specimen

|
M3#1065endocranial cast Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1065 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Agriochoerus sp. AMNH 95330 View specimen

|
M3#1067endocranial cast Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1067 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mouillacitherium elegans UM ACQ 6625 View specimen

|
M3#1068endocranial cast Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1068 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Caenomeryx filholi UM PDS 2570 View specimen

|
M3#1069endocranial cast Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1069 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Dichobune leporina MNHN.F.QU16586 View specimen

|
M3#1070endocranial cast Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1070 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Anoplotherium sp. not numbered View specimen

|
M3#1071endocranial cast Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1071 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
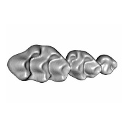
This contribution contains 3D models of upper molar rows of house mice (Mus musculus domesticus). The erupted part of the right row is presented for specimens belonging to four groups: wild-trapped mice, wild-derived lab offspring, a typical laboratory strain (Swiss) and hybrids between wild-derived and Swiss mice. These models are analyzed in the following publication: Savriama et al 2021: Wild versus lab house mice: Effects of age, diet, and genetics on molar geometry and topography. https://doi.org/10.1111/joa.13529
Mus musculus BW_03 View specimen

|
M3#736BW_03 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.736 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus BW_04 View specimen

|
M3#752BW_04 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.752 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus BW_06 View specimen

|
M3#753BW_06 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.753 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus BW_07 View specimen

|
M3#754BW_07 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.754 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus BW_08 View specimen

|
M3#755BW_08 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.755 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus BW_11 View specimen

|
M3#756BW_11 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.756 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus BW_12 View specimen

|
M3#757BW_12 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.757 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus Blab_035 View specimen

|
M3#758Blab_035 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.758 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus Blab_046 View specimen

|
M3#759Blab_046 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.759 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus Blab_054 View specimen

|
M3#760Blab_054 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.760 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus Blab_056 View specimen

|
M3#761Blab_056 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.761 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus Blab_082 View specimen

|
M3#762Blab_082 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.762 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus Blab_086 View specimen

|
M3#763Blab_086 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.763 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus Blab_092 View specimen

|
M3#764Blab_092 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.764 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus Blab_319 View specimen

|
M3#751Blab_319 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.751 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus Blab_325 View specimen

|
M3#750Blab_325 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.750 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus Blab_329 View specimen

|
M3#737Blab_329 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.737 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus Blab_330 View specimen

|
M3#738Blab_330 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.738 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus Blab_F2a View specimen

|
M3#739Blab_F2a Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.739 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus Blab_F2b View specimen

|
M3#740Blab_F2b Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.740 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus Blab_BB3w View specimen

|
M3#741Blab_BB3w Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.741 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus hyb_BS01 View specimen

|
M3#742hyb_BS01 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.742 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus hyb_BS02 View specimen

|
M3#743hyb_BS02 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.743 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus hyb_SB01 View specimen

|
M3#744hyb_SB01 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.744 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus hyb_SB02 View specimen

|
M3#745hyb_SB02 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.745 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus SW_001 View specimen

|
M3#746SW_001 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.746 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus SW_002 View specimen

|
M3#747SW_002 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.747 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus SW_005 View specimen

|
M3#748SW_005 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.748 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus SW_0ter View specimen

|
M3#749SW_0ter Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.749 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Mus musculus SW_343 View specimen

|
M3#765SW_343 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.765 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
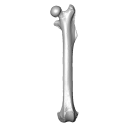
This 3D Dataset includes the 3D models analysed in Wölfer J & Hautier L. 2024 Inferring the locomotor ecology of two of the oldest fossil squirrels: influence of operationalisation, trait, body size, and machine learning method. Proceedings of the Royal Society B. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2024-0743
Palaeosciurus goti MGB125 View specimen

|
M3#1577Left femur of Palaeosciurus goti Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1577 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
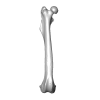
Palaeosciurus feignouxi GER291 View specimen
|
M3#1578Right femur of Palaeosciurus feignouxi Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1578 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
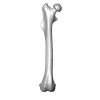
Palaeosciurus feignouxi GER293 View specimen
|
M3#1579Right femur of Palaeosciurus feignouxi Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1579 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Palaeosciurus feignouxi GER294 View specimen

|
M3#1580Right femur of Palaeosciurus feignouxi Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1580 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
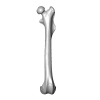
Palaeosciurus feignouxi GER296 View specimen
|
M3#1581Left femur of Palaeosciurus feignouxi Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1581 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
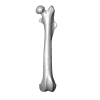
Palaeosciurus feignouxi GER298 View specimen
|
M3#1582Left femur of Palaeosciurus feignouxi Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1582 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Palaeosciurus feignouxi GER299 View specimen
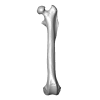
|
M3#1583Left femur of Palaeosciurus feignouxi Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1583 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
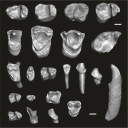
This contribution contains the three-dimensional digital models of the dental fossil material of anthropoid and strepsirrhine primates, discovered in Lower Oligocene detrital deposits outcropping in the Porto Rico and El Argoub areas, east of the Dakhla peninsula region (Atlantic Sahara; in the south of Morocco, near the northern border of Mauritania). These fossils were described, figured and discussed in the following publication: Marivaux et al. (2024), A new primate community from the earliest Oligocene of the Atlantic margin of Northwest Africa: Systematic, paleobiogeographic and paleoenvironmental implications. Journal of Human Evolution. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhevol.2024.103548
Catopithecus aff. browni DAK-Arg-087 View specimen

|
M3#1211Isolated right lower m3 (worn) Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1211 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Catopithecus aff. browni DAK-Arg-088 View specimen
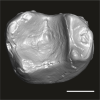
|
M3#1212Isolated right lower m2 (abraded/corroded) Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1212 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Catopithecus aff. browni DAK-Arg-089 View specimen
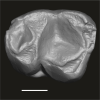
|
M3#1213Isolated left lower m1 (worn) Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1213 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Catopithecus aff. browni DAK-Pto-052 View specimen
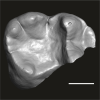
|
M3#1214Isolated right lower m1 (pristine but lacking the mesiobuccal region) Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1214 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Catopithecus aff. browni DAK-Arg-090 View specimen
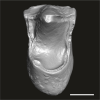
|
M3#1215Isolated left upper P4 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1215 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Catopithecus aff. browni DAK-Arg-091 View specimen
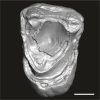
|
M3#1216Isolated left upper M2 (worn and corroded) Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1216 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Catopithecus aff. browni DAK-Pto-053 View specimen
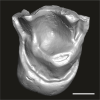
|
M3#1217Isolated right upper M1 (lacking the buccal region) Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1217 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Abuqatrania cf. basiodontos DAK-Arg-092 View specimen
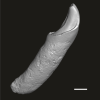
|
M3#1218Isolated left lower c1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1218 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
?Propliopithecus sp. DAK-Pto-056 View specimen
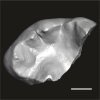
|
M3#1219Isolated right lower m3 (fragment of talonid of a germ) Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1219 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Abuqatrania cf. basiodontos DAK-Arg-093 View specimen
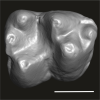
|
M3#1469Isolated right lower m1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1469 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Abuqatrania cf. basiodontos DAK-Arg-094 View specimen
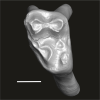
|
M3#1221Isolated left upper M1 or M2 (corroded, lacking the enamel cap [exposed dentine]) Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1221 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Abuqatrania cf. basiodontos DAK-Arg-095 View specimen
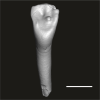
|
M3#1222Isolated right lower i1 or i2 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1222 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Abuqatrania cf. basiodontos DAK-Arg-096 View specimen
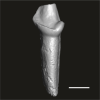
|
M3#1223Isolated right lower p2 (worn apex) Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1223 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Abuqatrania cf. basiodontos DAK-Arg-097 View specimen
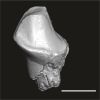
|
M3#1224Isolated right lower p2 (worn apex and broken root) Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1224 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Afrotarsius sp. DAK-Arg-098 View specimen
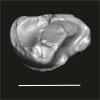
|
M3#1225Isolated left lower p3 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1225 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Afrotarsius sp. DAK-Pto-054 View specimen
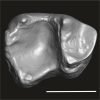
|
M3#1226Isolated right lower m1 (abraded/corroded) Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1226 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Orolemur mermozi DAK-Pto-055 View specimen
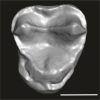
|
M3#1227Isolated right upper M1 or M2 (pristine, Holotype) Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1227 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Wadilemur cf. elegans DAK-Arg-099 View specimen
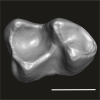
|
M3#1228Isolated right lower m2 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1228 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
cf. 'Anchomomys' milleri DAK-Arg-100 View specimen

|
M3#1229Isolated right lower c1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1229 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Abuqatrania cf. basiodontos DAK-Arg-101 View specimen
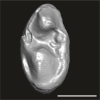
|
M3#1396Isolated left upper M3 (abraded) Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1396 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Orogalago saintexuperyi DAK-Arg-102 View specimen
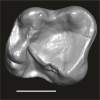
|
M3#1397Isolated left lower m2 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1397 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Wadilemur cf. elegans DAK-Arg-103 View specimen

|
M3#1473Isolated right upper M1 or M2 (lacking the mesial and buccal regions) Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1473 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

The present 3D Dataset contains the 3D models analyzed in Bianucci et al. 2023, A heavyweight early whale pushes the boundaries of vertebrate morphology, Nature. These include bones of the holotype of new species Perucetus colossus (MUSM 3248), as well as the articulated skeleton of Cynthiacetus peruvianus (holotype, MNHN.F.PRU10). The latter was used to estimate the total skeleton volume of P. colossus.
Perucetus colossus MUSM 3248 View specimen

|
M3#1131Thirteen vertebrae, rib, and innominate of Perucetus colossus (holotype, MUSM NNNN). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1131 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Cynthiacetus peruvianus MNHN.F.PRU10 View specimen

|
M3#1130Articulated skeleton of the holotype of Cynthiacetus peruvianus MNHN.F.PRU10 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1130 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
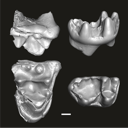
This contribution contains the three-dimensional digital models of eleven isolated fossil teeth of a merialine paroxyclaenid (Welcommoides gurki), discovered from lower Oligocene deposits of the Bugti Hills (Balochistan, Pakistan). These fossils were described, figured and discussed in the following publication: Solé et al. (2024), An unexpected late paroxyclaenid (Mammalia, Cimolesta) out of Europe: dental evidence from the Oligocene of the Bugti Hills, Pakistan. Papers in Palaeontology. https://doi.org/10.1002/spp2.1599
Welcommoides gurki UM-DBC 2225 View specimen
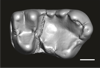
|
M3#1083Left m3 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1083 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Welcommoides gurki UM-DBC 2226 View specimen
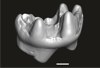
|
M3#1084Right m3 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1084 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
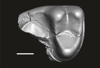
Welcommoides gurki UM-DBC 2227 View specimen
|
M3#1085Trigonid of a right lower molar Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1085 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
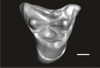
Welcommoides gurki UM-DBC 2230 View specimen
|
M3#1086Right DP4 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1086 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
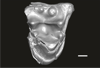
Welcommoides gurki UM-DBC 2228 View specimen
|
M3#1093Right M1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1093 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
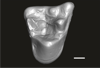
Welcommoides gurki UM-DBC 2229 View specimen
|
M3#1087Right M2 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1087 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
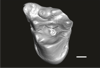
Welcommoides gurki UM-DBC 2236 View specimen
|
M3#1088Left M2 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1088 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
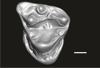
Welcommoides gurki UM-DBC 2231 View specimen
|
M3#1089Left M3 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1089 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
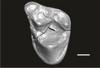
Welcommoides gurki UM-DBC 2232 View specimen
|
M3#1090Left M3 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1090 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
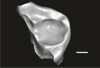
Welcommoides gurki UM-DBC 2234 View specimen
|
M3#1091Left M3 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1091 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Welcommoides gurki UM-DBC 2233 View specimen
|
M3#1092Left M3 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1092 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
The present 3D Dataset contains the 3D models analyzed in Keppeler, H., Schultz, J. A., Ruf, I., & Martin, T., 2023. Cranial anatomy of Hypisodus minimus (Artiodactyla: Ruminantia) from the Oligocene Brule Formation of North America. Palaeontographica Abteilung A.
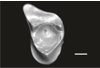
Hypisodus minimus SMNK-PAL 27212 View specimen
|
M3#1031CT image stack of a skull of Hypisodus minimus. Also includes a lumbar vertebra and a probable proximal phalanx of digit III or IV. Type: "3D_CT"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1031 state:published |
Download CT data |
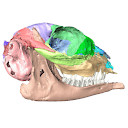
|
M3#10363D surface models of a skull of Hypisodus minimus (SMNK-PAL27212). The data includes a surface model for: basisphenoid, tympanic bullae, ethmoid (lamina perpendicularis), frontals, jugal (left), jugal (right), lacrimals, lower dentition, mandibles, mastoid processes, maxillaries, maxilloturbinals, nasals, occipital, palatine, parietals, petrosals, presphenoid, squamosals, turbinates, upper dentition, and the vomer. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1036 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
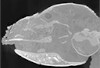
Hypisodus minimus SMNK-PAL 27213 View specimen
|
M3#1033CT image stack of a skull of Hypisodus minimus. Also shows numerous postcranial material including an atlas articulated with the occipital bone, the distal part of a left humerus articulated to radius and ulna, a part of a femur, a part of a tibia and fibula, unidentifiable tarsal bones, parts of the metatarsals II, III, IV and V and their phalanges, a proximal phalanx of digit III or IV, a middle phalanx of digit III or IV, a possible patella and calcaneus, as well as numerous unidentifiable broken bony fragments. Type: "3D_CT"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1033 state:published |
Download CT data |

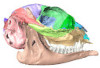
|
M3#10353D surface models of a skull of Hypisodus minimus (SMNK-PAL27213). The data includes a surface model for: atlas, basisphenoid, tympanic bullae, nasals, occipital, the petrosals, and the inner ear. Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1035 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
The present 3D Dataset contains the 3D models analyzed in: Kaigai N et al. Morphogenesis and three-dimensional movement of the stomach during the human embryonic period, Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2014 May;297(5):791-797. doi: 10.1002/ar.22833.
Homo sapiens KC-CS16STM27159 View specimen
|
M3#56computationally reconstructed stomach of the human embryo (M3#56_KC-CS16STM27159) at Carnegie Stage 16 (Crown Rump Length= 9.9mm). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf56 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS17STM20383 View specimen

|
M3#57computationally reconstructed stomach of the human embryo (M3#57_KC-CS17STM20383) at Carnegie Stage 17 (Crown Rump Length= 12.3mm). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf57 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS18STM21807 View specimen

|
M3#58computationally reconstructed stomach of the human embryo (M3#58_KC-CS18STM21807) at Carnegie Stage 18 (Crown Rump Length= 14.7mm). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf58 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS19STM17998 View specimen

|
M3#59computationally reconstructed stomach of the human embryo (M3#59_KC-CS19STM17998) at Carnegie Stage 19 (Crown Rump Length was unmeasured ). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf59 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS20STM20785 View specimen

|
M3#60computationally reconstructed stomach of the human embryo (M3#60_KC-CS20STM20785) at Carnegie Stage 20 (Crown Rump Length= 18.7 mm). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf60 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS21STM24728 View specimen

|
M3#61computationally reconstructed stomach of the human embryo (M3#61_KC-CS21STM24728) at Carnegie Stage 21 (Crown Rump Length= 20.9 mm). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf61 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS22STM26438 View specimen

|
M3#62computationally reconstructed stomach of the human embryo (M3#62_KC-CS22STM26438) at Carnegie Stage 22 (Crown Rump Length= 21.5 mm). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf62 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens KC-CS23STM20018 View specimen

|
M3#63computationally reconstructed stomach of the human embryo (M3#63_KC-CS23STM20018) at Carnegie Stage 23 (Crown Rump Length= 23.1 mm). Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf63 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
This contribution contains the three-dimensional digital models of the dental fossil material of strepsirrhine primates (Azibiidae and ?Djebelemuridae) from the late early to early middle Eocene of the Gour Lazib Complex in western Algeria and of Djebel Chambi in central-western Tunisia. These fossils were described, figured and discussed in the following publication: Marivaux et al. (2025), New insights into the diversity of strepsirrhine primates from the late early – early middle Eocene of North Africa (Algeria and Tunisia). Journal of Human Evolution, 103729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhevol.2025.103729
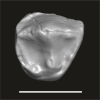
Algeripithecus minimissimus ONM-CBI-1-38 View specimen
|
M3#1715Isolated right P3 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1715 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
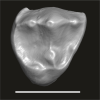
Algeripithecus minimissimus ONM-CBI-1-37 View specimen
|
M3#1716Isolated right P4 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1716 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
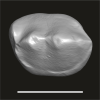
Algeripithecus minimissimus ONM-CBI-1-1206 View specimen
|
M3#1717Isolated right p4 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1717 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
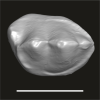
Algeripithecus minimissimus ONM-CBI-1-1207 View specimen
|
M3#1718Isolated right p4 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1718 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Algeripithecus minimissimus ONM-CBI-1-1205 View specimen
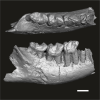
|
M3#1719Fragment of right mandible bearing m1-3 (Holotype) Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1719 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Algeripithecus minimissimus ONM-CBI-1-1209 View specimen
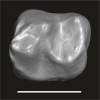
|
M3#1720Isolated left m2 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1720 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Algeripithecus minimissimus ONM-CBI-1-1208 View specimen
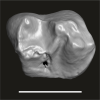
|
M3#1721Isolated right m2 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1721 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Algeripithecus minutus UM-HGL50-294 View specimen
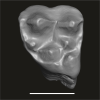
|
M3#1722Left DP4 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1722 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Algeripithecus minutus UM-HGL50-297 View specimen
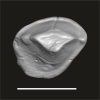
|
M3#1723Isolated right P2 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1723 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Algeripithecus minutus UM-HGL50-298 View specimen
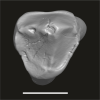
|
M3#1724Isolated right P3 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1724 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Algeripithecus minutus UM-HGL50-299 View specimen
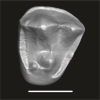
|
M3#1725Isolated right P4 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1725 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Algeripithecus minutus UM-HGL50-303 View specimen
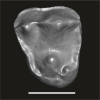
|
M3#1726Isolated left P4 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1726 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
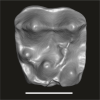
Algeripithecus minutus UM-GZC-7 View specimen
|
M3#1727Isolated left M1 (lingually broken) Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1727 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
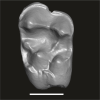
Algeripithecus minutus UM-GZC-1 View specimen
|
M3#1728Isolated left M2 (Holotype) Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1728 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
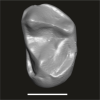
Algeripithecus minutus UM-HGL50-319 View specimen
|
M3#1729Isolated left M3 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1729 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
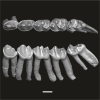
Algeripithecus minutus UM-HGL50-397 View specimen
|
M3#1730Fragment of left mandible bearing p3-m3 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1730 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
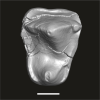
Azibius magnus UM-HGL50-258 View specimen
|
M3#1731Isolated right P3 or P4 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1731 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
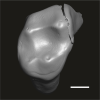
Azibius magnus UM-HGL50-260 View specimen
|
M3#1732Isolated right M2 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1732 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
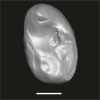
Azibius magnus UM-HGL50-261 View specimen
|
M3#1733Isolated left M3 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1733 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Azibius magnus UM-HGL50-263 View specimen

|
M3#1734Isolated left p3 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1734 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
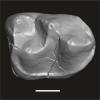
Azibius magnus UM-HGL50-264 View specimen
|
M3#1735Isolated right m1 (Holotype) Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1735 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
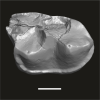
Azibius magnus UM-HGL50-265 View specimen
|
M3#1736Isolated right m1 (lingually broken) Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1736 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
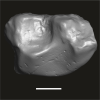
Azibius magnus UM-HGL50-266 View specimen
|
M3#1738Isolated right m2 (corroded) Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1738 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
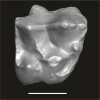
Azibius trerki UM-HGL50-166 View specimen
|
M3#1739Isolated right DP4 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1739 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
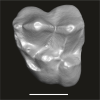
Azibius trerki UM-HGL50-295 View specimen
|
M3#1740Isolated left DP4 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1740 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
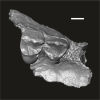
Azibius trerki UM-HGL51-46 View specimen
|
M3#1741Fragment of right maxillary bearing P3-4 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1741 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
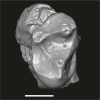
|
M3#1742Fragment of right maxillary bearing M3 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1742 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
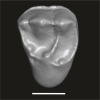
Azibius trerki UM-GZC-41 View specimen
|
M3#1743Isolated left P4 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1743 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
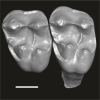
Azibius trerki UM-HGL50-396 View specimen
|
M3#1744Boneless fragment of a left maxillary bearing M1-2 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1744 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Azibius trerki UM-HGL50-270 View specimen
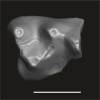
|
M3#1745Fragment (talonid) of an isolated right dp4 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1745 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Azibius trerki UM-HGL50-248 View specimen
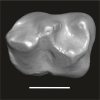
|
M3#1746Isolated left m1 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1746 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Azibius trerki UM-HGL50-256 View specimen

|
M3#1753Fragment of left mandible bearing p4-m3 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1753 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Lazibadapis anchomomyinopsis UM-HGL50-326 View specimen
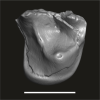
|
M3#1747Isolated right M1 (buccally broken) Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1747 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Lazibadapis anchomomyinopsis UM-HGL50-169 View specimen
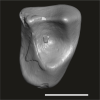
|
M3#1748Isolated right M2 (corroded) Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1748 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
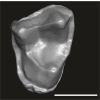
Lazibadapis anchomomyinopsis UM-HGL50-170 View specimen
|
M3#1749Isolated right M2 or M3 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1749 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
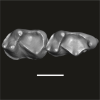
Lazibadapis anchomomyinopsis UM-HGL50-325 View specimen
|
M3#1750Boneless fragment of left mandible preserving m2-3 (Holotype) -> m2 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1750 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
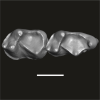
|
M3#1751Boneless fragment of left mandible preserving m2-3 (Holotype) -> m3 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1751 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Lazibadapis anchomomyinopsis UM-HGL50-290 View specimen
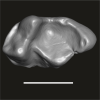
|
M3#1752Isolated left m3 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1752 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
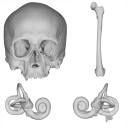
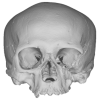
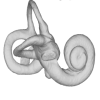
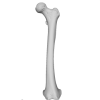
The present 3D Dataset contains the models analyzed in the publication: Menéndez L, Rios C, Acosta Morano C, Novellino P, Schmelzle T, Aguirre-Fernández G, Breidenstein A, Barquera R, Schuenemann VJ, Stafford TW, Sánchez-Villagra M, Barbieri C. (2025). A human skeleton from Última Esperanza, South-West Patagonia, Chile: Osteobiography, morphometric, and genetic analysis. The models include the skull, femur, and the segmented left and right inner ears of a late Holocene human skeleton from southern Patagonia. In the associated paper, we present the radiocarbon dating, an osteobiography profile evaluating some aspects of the life history of this individual, as well as genetic and morphometric analysis assessing biological relatedness to other individuals and populations.
Homo sapiens PIMUZ A/V 4612 View specimen
|
M3#1650Homo sapiens skull Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1650 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#1652Homo sapiens left inner ear Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1652 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
|
M3#1653Homo sapiens right inner ear Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1653 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Homo sapiens PIMUZ A/V 4613 View specimen
|
M3#1651Homo sapiens femur Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1651 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

This contribution contains the 3D models described and figured in the following publication: Pujos F., Hautier L., Antoine P-O., Boivin M., Moison B, Salas-Gismondi R, Tejada J.V. , Varas-Malca R.M., Yans J., Marivaux L. (2025). Unexpected pampatheriid from the early Oligocene of Peruvian Amazonia: insights into the tropical differentiation of cingulate xenarthrans. Historical Biology.
Bradypus tridactylus UM-ZOOL-V69 View specimen

|
M3#1600Molariform and associated dentinal microstructure Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1600 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Choloepus didactylus UM-ZOOL-V12 View specimen

|
M3#1601Molariform and associated dentinal microstructure Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1601 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Dasypus mexicanus UM-ZOOL-2787 View specimen

|
M3#1602Molariform and associated dentinal microstructure Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1602 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Tolypeutes matacus UM-ZOOL-2789 View specimen

|
M3#1603Molariform and associated dentinal microstructure Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1603 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Euphractus sexcinctus UM-ZOOL-2790 View specimen

|
M3#1604Molariform and associated dentinal microstructure Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1604 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Holmesina septrionalis UM-FLD-1 View specimen

|
M3#1605Molariform and associated dentinal microstructure Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1605 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Megatherium sp. UM-TAR-1 View specimen

|
M3#1607Molariform and associated dentinal microstructure Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1607 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
Indet indet MUSM-3965 View specimen
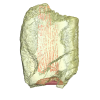
|
M3#1606Molariform and associated dentinal microstructure Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1606 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
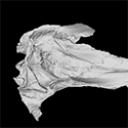
The present 3D Dataset contains the 3D model analyzed in The largest freshwater odontocete: a South Asian river dolphin relative from the Proto-Amazonia.
Pebanista yacuruna MUSM 4017 View specimen

|
M3#1394Holotype skull of Pebanista yacuruna MUSM 4017 Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1394 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |
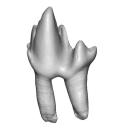
This contribution contains the 3D model described and figured in the following publication: Martin, T., Averianov, A. O., Schultz, J. A., & Schwermann, A. H. (2023). A stem therian mammal from the Lower Cretaceous of Germany. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology, e2224848.
Spelaeomolitor speratus WMNM P99101 View specimen
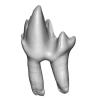
|
M3#12573D_model_Spelaeomolitor_lower_molar Type: "3D_surfaces"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1257 state:published |
Download 3D surface file |

|
M3#1258CT imagestack (jpgs) and info data sheet (pca file) in one zip folder Type: "3D_CT"doi: 10.18563/m3.sf.1258 state:published |
Download CT data |